Applications and systems rely on smooth communication and data sharing to deliver improved functionality and services in today's interconnected digital environment. Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) are quite important in this situation. APIs serve as mediators, enabling interoperability, data sharing, and communication between various software programmes. This article will provide you a thorough introduction to APIs and their importance in contemporary software development, whether you're a developer, a tech enthusiast, or just interested about the world of APIs.
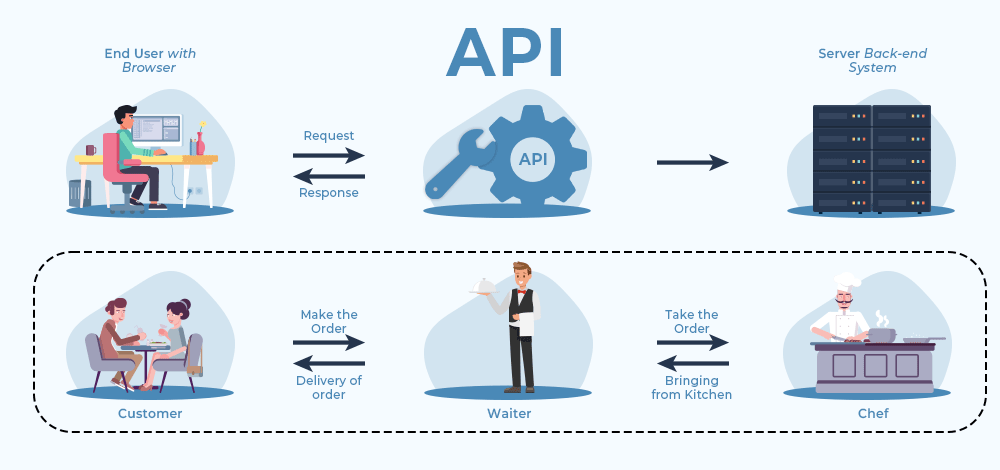
Introduction to API
Application Programming Interface is referred to as API. It is a set of guidelines and protocols that specifies how various software components ought to communicate and share information.
- APIs can be thought of as a contract that enables successful communication between two software entities.
- APIs give programmers a standardised method of using the features of other software platforms, libraries, or systems.
Why are APIs Important?
APIs have revolutionized the way software is developed and integrated. Here are some key reasons why APIs are important:
- Seamless Integration
- Extensibility and Scalability
- Collaboration and Innovation
- User Experience
By allowing various software systems to interact and cooperate, APIs enable developers to take advantage of already-existing functions and resources without having to start from scratch.
APIs give software developers a modular way to create new features, services, or data sources. As applications can be built upon existing APIs, promoting extensibility and scalability while saving time and effort.
By offering a standardised method of sharing data and services, APIs promote collaboration between developers and organisations. As a result, innovation is accelerated since developers can use APIs to build new apps or incorporate current systems into creative solutions.
APIs make it easier to incorporate services or data sources from outside sources into applications, which improves the overall user experience. For instance, incorporating a weather API into a travel app gives users access to real-time weather information, enhancing the utility and appeal of the service.
Types of APIs
APIs come in different types and formats, depending on the purpose and underlying technology. Here are some common types of APIs:
Web APIs: These APIs allow web-based services and applications to communicate with one another. The majority of the time, they are built on widely used web protocols like
HTTPandREST(Representational State Transfer).SOAP APIs: Based on XML (eXtensible Markup Language), SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol) APIs offer a standardised method for applications to communicate structured information across a network.
JSON-RPC and XML-RPC: JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) or XML can be used as the data format for remote procedure calls when using the
JSON-RPCorXML-RPC APIs. They're frequently employed for lightweight.
API Communication Styles:
RESTful APIs: REST (Representational State Transfer) is a popular architectural style for designing web APIs. RESTful APIs use standard HTTP methods such as
GET,POST,PUT, andDELETEto perform operations on resources. They often return data in formats like JSON or XML.GraphQL: GraphQL is an alternative to RESTful APIs that provides a more flexible and efficient approach to data retrieval. With GraphQL, clients can specify the exact data they need, reducing over-fetching and under-fetching of data.
Real-Time APIs: Real-time APIs use technologies like WebSockets to enable bidirectional communication between the client and the server. They are ideal for applications that require instant updates, such as chat applications or real-time collaboration tools.
Common APIs
Social media APIs: Websites like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram offer APIs that let programmers incorporate social media features into their applications, such as updating statuses, retrieving user profiles, or engaging with social networks.
Payment Gateway APIs: Companies such as PayPal, Stripe, and Braintree provide APIs for handling online payments, allowing developers to include secure payment processing into their apps.
Mapping and Geolocation APIs: Maps, geolocation data, routing, and other location-based services are all made available by mapping and geolocation APIs, which developers can use to build apps with mapping features. Examples of these APIs include Google Maps and Mapbox.
Conclusion
APIs enable seamless integration, teamwork, and creativity, serving as the foundation for contemporary software development. For developers and organisations wishing to take use of the power of APIs to build strong and interconnected applications, understanding APIs and their many types, communication styles, authentication methods, documentation practises, and management systems is essential. So go ahead and discover the immense possibilities that APIs contain for your software applications by exploring their enormous world!
